The Leadership Styles Handbook:
Finding the Style That Works Best For You and Your Team
Given how incredibly nuanced people leadership is, it should not be surprising that there is no single way to answer the "which leadership style is best" question. In this downloadable guide, you'll find a high-level overview of the 6 most common leadership styles so you can then decide which is best to adopt for you and your team at any given time.
Download the PDF (English & French Included)
Introduction
Everyone wants to know which style is considered the best and the worst when it comes to leadership styles. It’s a question thousands of people type into Google every year, and pages upon pages of search results seek to answer. Unfortunately, if you do this, you’re likely to end up more confused than when you started because, as you’ll quickly find out, there is no one answer to the question.
That’s because leadership is so incredibly nuanced. For example, what works for a supervisor leading a team on the frontline of a manufacturing plant may be entirely different from their counterpart in the customer service or marketing department. In fact, these two leaders could argue until they’re blue in the face over which of their leadership styles is better and never come to an agreement.
So, what does this mean for you? First, it means that you can relax knowing there is no wrong answer when it comes to adopting a leadership style (or styles!), as it will entirely depend on the nature of your work, your company’s culture, and those in your charge. Second, it means that finding your leadership style is not something that will happen overnight. Rather, it’s a process and your style will evolve as you do over the course of your career in leadership.
To get started, take the following quiz to find out your current dominant leadership style. Then, read through the guide to get a better understanding of not just that style, but the others as well. Also, as you read through each, think about a time when you adopted a given style - How did you feel? Was it effective? What were the circumstances? Think about your past leaders or mentors you look up to or want to emulate - Which style did they embody? Even consider the type of leader you want to be in 6 months or 6 years. In doing this, you will find yourself one step closer to knowing which leadership style is best for you.
The Charismatic Leadership Style
Charismatic leaders use various communication techniques to build strong emotional connections and interpersonal relationships, leading by example, and influencing others and fulfilling their mandate. They are the leaders who make employees feel that they can achieve a goal or milestone even in the face of adversity and who keep a positive attitude and encourage others to keep going when things get tough. According to a study in the Journal of Behavioral Studies in Business, they do this by using the following four techniques:
- Humor - Self-deprecating humor is commonly used as a tool to show vulnerabilities, increase likability, “level the playing field,” and lower people’s guard, which contributes to the creation of an emotional bond.
- Storytelling - The use of stories that include audience members or are humorous or self-deprecating is often used to illustrate a message, so the audience can better retain the information or instruction.
- Reading the Audience - A charismatic leader observes or “reads” their audience's facial expressions, body language, and tone of voice to determine if a humorous story, dramatic pause, or change in cadence or tone is most appropriate.
- Working the Room - By shaking hands, learning names, asking personal questions, actively listening, and generally connecting with the audience on a one-to-one basis, charismatic leaders get a “feel” of the room, which they can then use to alter their styles and techniques for optimal impact.
The Advantages of Charismatic Leadership
-
Increased sense of belonging as a result of the employee’s emotional connection with their leader. (Cambridge University Press)
-
Charismatic leadership is positively related to an individual’s identification with their workgroup or team, positively contributing to job involvement, job satisfaction, performance, and turnover intention. (International Journal of Psychology)
-
The strong emotional connections and relationships charismatic leaders build with their employees can create a sense of trust and loyalty.
-
Improved teamwork results from charismatic leaders' strategic vision, clear and articulate communication, sensitivity to the environment, and sensitivity to employee needs. (Leadership and Organization Development Journal)
-
Employees led by charismatic leaders show signs of reduced stress and burnout. (University of London and University of Hertfordshire)
The Possible Disadvantages of Charismatic Leadership
-
Employees may become too reliant on their charismatic leader to set the vision, tell them what to do or feel, and even motivate them.
-
When charismatic leaders put exceptionally high-performance pressure on employees, employees may behave unethically to meet the set expectations. (International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health)
-
Charismatic leadership can be misused, manipulated, or abused to get what an individual wants or to further a personal agenda. (The Business and Management Review)
The Democratic/Participative Leadership Style
Unlike the leadership styles that operate using a top-down approach, the democratic leadership style, also referred to as participative leadership, forgoes the formal, hierarchical structure in favor of collaboration, teamwork, consensus, and participation from all. While democratic leaders prefer to work with their teams as equals and hear out all voices, they retain the formal authority and responsibility to make decisions they feel best to align with the interests of the team, client, or organization. Interestingly, in one study, 70% of respondents disagreed that this leadership style results in many problems in the workplace; rather, about the same percentage affirmed that democratic/participative leadership is more effective than autocratic and free rein leadership styles.
The Advantages of Democratic Leadership
-
Democratic leadership builds high levels of trust, which leads employees to reciprocate through exhibiting higher levels of organizational performance. (International Journal of Development Strategies)
-
Given the nature of democratic leadership, it can support creating an inclusive and collaborative team culture as an emphasis is put on everyone being heard.
-
Democratic leadership increases employee satisfaction and organizational efficiency, thus positively influencing the success of the organization. (Canadian Journal of Business and Information Studies)
-
Democratic/participative leadership is associated with increased creativity and problem-solving. (Journal of Developmental Entrepreneurship)
-
The democratic leadership style is likely to engage and empower individuals due to feeling valued by their leader.
The Possible Disadvantages of Democratic Leadership
-
The decision-making process is inevitably slowed down or overly complicated as democratic leaders seek out and contemplate many perspectives, which can be particularly problematic in crises where decisions need to be made quickly.
-
Employees may consciously or unconsciously resent a leader’s decision if they feel their perspective is not adequately considered. For that reason, democratic leaders should be prepared to explain the rationale for a decision to an appropriate extent.
-
If democratic leaders appear to take one individual's “side” or perspective too often, it can be interpreted as favoritism which can, in turn, cause tension.
The Laissez-Faire Leadership Style
Laissez-faire leaders typically take a hands-off approach to managing others and seek to limit their interference with the day-to-day activities of those around them. However, this absence does not absolve them of responsibility for their employee’s behaviors, actions, and outcomes. The most effective laissez-faire leaders realize this and are prepared to step up when their team needs it.
As you can imagine, this leadership style is risky in the wrong circumstances, such as when employees are new or untrained. On the other hand, laissez-faire leadership can be highly effective for those managing highly trained teams of experts, creative departments or projects, or employees with a track record of success, accountability, and motivation.
The Advantages of Laissez-Faire Leadership
-
Reduces an employee's dependence on the leader as the absence of a leader challenges them to find answers, proactively problem-solve, and make decisions independently.
-
Employees learn new skills and establish interpersonal relationships they may not otherwise have in order to fulfill the mandate.
-
Potentially reduces the amount of time a leader spends directly managing people, which could mitigate micromanagement.
-
Certain employees will be challenged, motivated, and empowered by the freedom and control they have over their work and life on the job under a laissez-faire leader.
-
Can lead to an increased number of unique learning and development opportunities that engage employees.
The Possible Disadvantages of Laissez-Faire Leadership
-
Laissez-faire leaders who withhold reinforcement, constructive feedback, or praise, either intentionally or unintentionally, negatively impact their employee’s performance in one of two ways; they either decrease the probability of future desired behavior or open the door for increased levels of undesired performance. (European Journal of Management)
-
Individuals whose sense of self is strongly tied to their interpersonal relationships may experience laissez-faire leadership as disappointing, resulting in negative attitudes toward their supervisors and the organization. (Journal of Business and Psychology)
-
Laissez-faire leadership has been found to have a negative relationship with innovation and engagement at work. (Heliyon)
Get Your PDF
Save This For Later
After filling out the form, we will send you to the PDF version and also a copy to your email so you can file it away or share it with your colleagues.
The Autocratic/Authoritarian Leadership Style
Autocratic leadership, also known as authoritarian leadership, is characterized by a leader’s control and an employee’s obedience. A leader who adopts this style wields their formal authority to get things done a specific way or make decisions independently. While autocratic leadership may be less prevalent today and less preferred by employees, it is not necessarily an inherently bad leadership style. When a leader manages inexperienced, untrained, or unengaged employees, autocratic leadership may be the leadership style needed to get the work done on time and as promised. Furthermore, certain departments, such as customer service or manufacturing, or industries, such as food services and construction, may find the autocratic style more effective given the nature of the work.
The Advantages of Autocratic/Authoritarian Leadership
-
Authoritarian/autocratic leadership curbs deviant interpersonal behaviors. (University of Sheffield)
-
It makes the decision-making process arguably more timely and convenient as only one perspective is considered - the leaders.
-
It creates a sense of certainty and reassurance as employees know exactly what is expected of them and how to do it.
-
Reduces confusion within the team and larger organization as decision-making is centralized.
-
When leading an inexperienced or unengaged team, autocratic leadership ensures a level of quality and productivity.
The Possible Disadvantages of Autocratic/Authoritarian Leadership
-
When team leaders exhibit authoritarian/autocratic leadership behaviors, it can be detrimental to the psychological safety of employees and colleagues. (McKinsey)
-
Autocratic leaders who do not delegate tasks or try to maintain control over everything may find themselves stressed, working too much, or burnt out, which negatively impacts their ability to be effective leaders.
-
Authoritarian/autocratic leaders have been found to inhibit employee creativity by increasing employee fear and defensive silence. (Journal of Business Research)
The Pacesetting Leadership Style
As the name of this leadership style implies, pacesetting leadership is when a leader sets the pace for the team and expects their employees to meet their benchmark. Pacesetting leaders are keen to find ways to do their work better and faster; thus, the expected level of performance is perpetually being raised. Unfortunately, research regarding leadership styles often shows that this style cannot be maintained long-term without negatively impacting employee morale and team culture.
The Advantages of Pacesetting Leadership
-
Pacesetting leadership can be helpful when trying to achieve short-term goals as it can lead to a boost in productivity that is needed to get the work done.
-
Employees may be motivated or engaged by the demands and expectations set by pacesetting leaders.
-
Pacesetting leadership challenges employees to continuously improve their skills and processes to meet performance expectations.
-
Focusing on delivering results and meeting expectations, a pacesetting leader does not want conflict to impede their team’s progress. Therefore, they are quick to resolve conflicts.
-
Employees who are highly-trained experts, motivated, accountable, and hungry to perform at their best typically thrive under a pacesetting leader.
The Possible Disadvantages of Pacesetting Leadership
-
The pacesetting leadership style is difficult to maintain long-term. The demands it places on employees can eventually make them feel overwhelmed or burnt out, thus leading to a drop in their morale. (American Express)
-
The expectations of pacesetting leaders may make employees fear failure or risks, which can ultimately impact creativity and innovation.
-
Pacesetting leaders may not have the patience or time to provide coaching and constructive feedback to underperforming employees. This can lead to employees struggling unnecessarily.
The Affiliative Leadership Style
A people-first mentality defines the affiliative leadership style. Affiliative leaders focus on keeping their employees happy, forging emotional bonds, creating (and maintaining!) harmony, which creates a strong sense of belonging and psychological safety for their employees. Given this, the affiliative leadership style is optimal for situations where trust or relationships are broken and need to be mended. Granted, leaders who adopt this still may become too focused on “keeping the peace” to pacify those involved in conflict rather than nurture healthy conflict.
The Advantages of Affiliative Leadership
-
The affiliative leadership style can help repair a relationship and rebuild broken trust.
-
Collaboration among employees typically improves under affiliative leadership.
-
As a result of the strong relationships affiliative leaders build with others, employees may feel confident enough to problem-solve, innovate, and take calculated risks.
-
Affiliative leadership contributes positively to the culture, morale, and dynamics of a team.
-
The relationship an employee has with an affiliative leader and its sense of belonging may improve an employee’s level of engagement and likelihood of staying at the company.
The Possible Disadvantages of Affiliative Leadership
-
Given that affiliative leaders focus on harmony, any conflict may be seen as a threat, even if the conflict is healthy and necessary to move the team forward. As such, leaders may become too focused on eliminating the conflict rather than resolving it.
-
Affiliative leadership is not conducive to emergencies or urgent work, as it may significantly slow down the process and jeopardize the goal.
-
Employees may not receive the constructive feedback or correct performance discussions they need from their leader, leading to a decline in their performance.
Get Your PDF
Save This For Later
After filling out the form, we will send you to the PDF version and also a copy to your email so you can file it away or share it with your colleagues.
Is Situational Leadership the Answer?
After diving into more detail about each of the six major leadership styles, you will see there are pros and cons to each. As such, no one style is better than the other. Instead, those in people management positions need to take an agile approach to their leadership style.
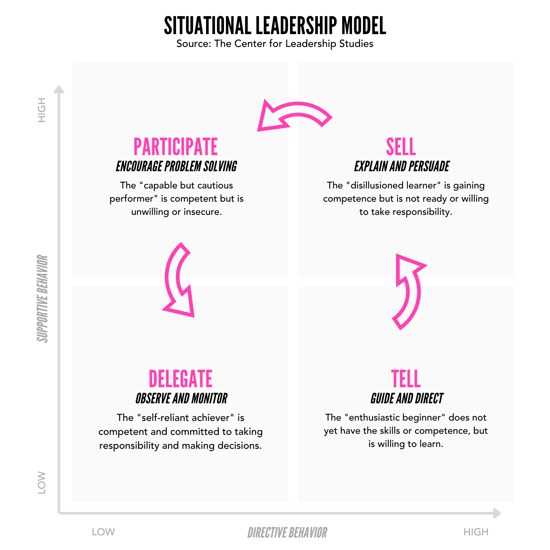
This approach is known as situational leadership, originally put forth by author Paul Hersey and leadership expert Ken Blanchard. Situational leadership is when a leader changes their leadership style based on the employee’s and the task to be completed. For example, the following model indicates that a new employee with little to no training yet is eager to learn might benefit from autocratic leadership. As their competence grows and the situation changes, the leadership style must change and adapt in turn.
Next Steps
To do this effectively, you will need to become a well-rounded leader with the knowledge and insight to understand which leadership style is appropriate to deploy, a variety of leadership skills, and tools that allow you to shift your style as the situation you find yourself in demands. Fortunately, Niagara Institute is here to help you do exactly that. With leadership development and communication training programs, and a full roster of professional coaches, you will be sure to find all the resources you need, when you need them, to become the leader you truly want to be.
Get Your PDF
Save This For Later
After filling out the form, we will send you to the PDF version and also a copy to your email so you can file it away or share it with your colleagues.

